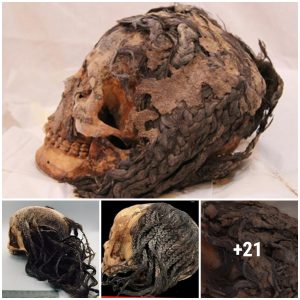
Archaeologists excavating in Arene Candide Cave have discovered evidence humans may have ritualistically “killed” pebbles to remove their symbolic power about 12,000 years ago. Skeleton of a man discovered at Arene Candide. The man’s head head was surrounded by hundreds of perforated shells
This discovery sheds new light on ancient burial practices and offers evidence of intentional fragmentation of objects in a ritual context some 5,000 years earlier than previously thought.

The Arene Candide Cave, located in northwestern Italy directly overlooking the Mediterranean, midway between Genoa and the French border contains a necropolis of some 20 adults and children. The cave is situated 90 meters above the sea in a steep cliff overlooking a limestone quarry. Arene Candide means “white sands,” referring to a sand dune that once lay against the cliff.
In the 1940s, archaeologists became interested in the cave and first excavations were conducted.
In 1942, a spectacular Mid Upper Palaeolithic (Gravettian) burial ornamented with shells was discovered at Arene Candide.
Nicknamed the Prince (“Il Principe”), the burial contained a skeleton of an adult man whose head was surrounded by hundreds of perforated shells and canines of deer, probably originally forming a kind of cap. The cave has given scientists a unique look at what life what life as far back as 40,000 years ago.

Today the Arene Candide Cave is considered a reference site for the Neolithic and Paleolithic periods in the western Mediterranean.Many intriguing fins have been made in the cave, but until now no-one bothered to investigate broken pebbles and learn if they were of importance to our ancestors.
Researchers at Université de Montréal, Arizona State University and University of Genoa have now examined 29 pebble fragments recovered from the cave and they tell a very interesting story about ancient burial practices.
A study of the objects reveals that some 12,000 years ago the flat, oblong pebbles were brought up from the beach, used as spatulas to apply ochre paste to decorate the dead, then broken and discarded.
The intent could have been to “kill” the tools, thereby “discharging them of their symbolic power” as objects that had come into contact with the deceased, said Julien Riel-Salvatore, an associate Professor of anthropology at UdeM who directed the excavations at the site that yielded the pebbles.
“If our interpretation is correct, we’ve pushed back the earliest evidence of intentional fragmentation of objects in a ritual context by up to 5,000 years,” said the study’s lead author Claudine Gravel-Miguel, a PhD candidate at Arizona State’s School of Human Evolution and Social Change, in Tempe.
“The next oldest evidence dates to the Neolithic period in Central Europe, about 8,000 years ago. Ours date to somewhere between 11,000 and 13,000 years ago, when people in Liguria were still hunter-gatherers.”
No matching pieces to the broken pebbles were found, prompting the researchers to hypothesize that the missing halves were kept as talismans or souvenirs. “They might have signified a link to the deceased, in the same way that people today might share pieces of a friendship trinket, or place an object in the grave of a loved one,” Riel-Salvatore said. “It’s the same kind of emotional connection. “This demonstrates the underappreciated interpretive potential of broken pieces,” the new study concludes. “Research programs on Paleolithic interments should not limit themselves to the burials themselves, but also explicitly target material recovered from nearby deposits, since, as we have shown here, artifacts as simple as broken rocks can sometimes help us uncover new practices in prehistoric funerary canons.
“Ancient people were not as primitive as many of us think. Ancient burial practices often involved complex rituals and ceremonies. Archaeologists have discovered evidence that Neanderthals made symbolic or ornamental objects, deliberately buried their dead. Sometimes they also marked their graves with offerings, such as flowers. No other primates, and no earlier human species, had ever practiced this sophisticated and symbolic behavior.
This unexpected behavior has made many researchers wonder if the Neanderthals also practiced religion.