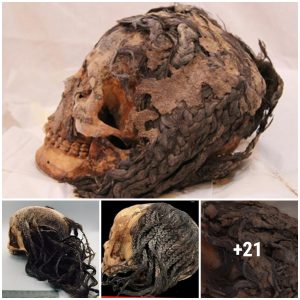
A hair sample from an ancient trophy head found buried in Peru reveals that the victim consumed a psychoactive plant prior to death. Thousands of years ago, a child in Peru was sacrificed as part of an ancient ritual, their head severed at the neck and made into a type of trophy. A new analysis of a single hair plucked from the mummy’s skull reveals that the child consumed a psychoactive cactus prior to execution, as part of the ceremony.
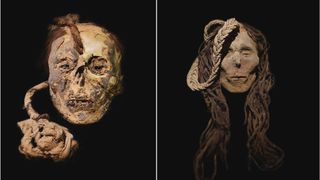
The child’s preserved head was one of 22 human remains associated with the ancient Nazca society examined in a new study; all of these individuals lived during the pre-Hispanic era (3500 B.C. to A.D. 476) and were buried near the southern coast of Peru, where they were excavated during the Nazca Project, a long-running archaeological program that began in 1982. While scientists are uncertain of the child victim’s sex and age at death, they reported that the child had ingested San Pedro cactus (Echinopsis pachanoi), a prickly plant taken for its “strong hallucinogenic properties” and used by indigenous civilizations of the Americas in traditional medicines and during rituals.
“The trophy head is the first case of the consumption of San Pedro by an individual living on the southern Peruvian coast,” study lead author Dagmara Socha, a doctoral candidate in the Center for Andean Studies at the University of Warsaw in Poland, told Live Science. “It’s also the first evidence that some of the victims who were made into trophy heads were given stimulants before they died.”For the study, Socha and her team collected samples of individual hairs from four trophy heads, three of which belonged to adults, and from 18 mummies of both adults and children. Toxicological examinations revealed that many of the deceased had consumed some type of psychoactive or stimulant plant prior to their deaths.
The drug use dated from 100 B.C. to A.D. 450, the researchers found. “We can see this transition of the plants was beginning early and we can actually trace the trade network,” Socha said. “Our research shows that these plants were extremely important to different cultures for medical or visionary effect. Especially since there’s no [written record] from this time period, so what we know about Nazca and other nearby cultures is from archaeological investigations.” Sixteen years prior to this study, Rainer Bussmann, a professor in the Department of Ethnobiology at the Institute of Botany at Ilia State University in Tbilisi, Georgia, and the head of botany at the State Museum of Natural History Stuttgart in Germany, published a study in the Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine examining medicinal plant usage by indigenous communities in northern Peru. Like Socha, he examined trade routes of different cultivated plants in this part of the world.
“There was always a little trade going on in this region, with plants being traded from the Amazon up and down the [Peruvian] coast,” Bussmann, who was not involved in the new study, told Live Science. “These plants were traditionally used for ceremonial or medicinal purposes, and [were] sometimes combined. I’ve never seen any reports of recreational use. For these cultures, there was always a specific purpose.”
But while evidence suggests that these plants were consumed as medicines and for ceremonies, scientists still have questions about how widespread consumption was within the Nazca culture, Socha said. “We actually don’t know how often these [plants] were being used,” she said. “In the case of San Pedro, it’s not well preserved in an archaeological context, and in the case of the coca leaves and Banisteriopsis caapi, they were never found to be growing in this region during that time period.”
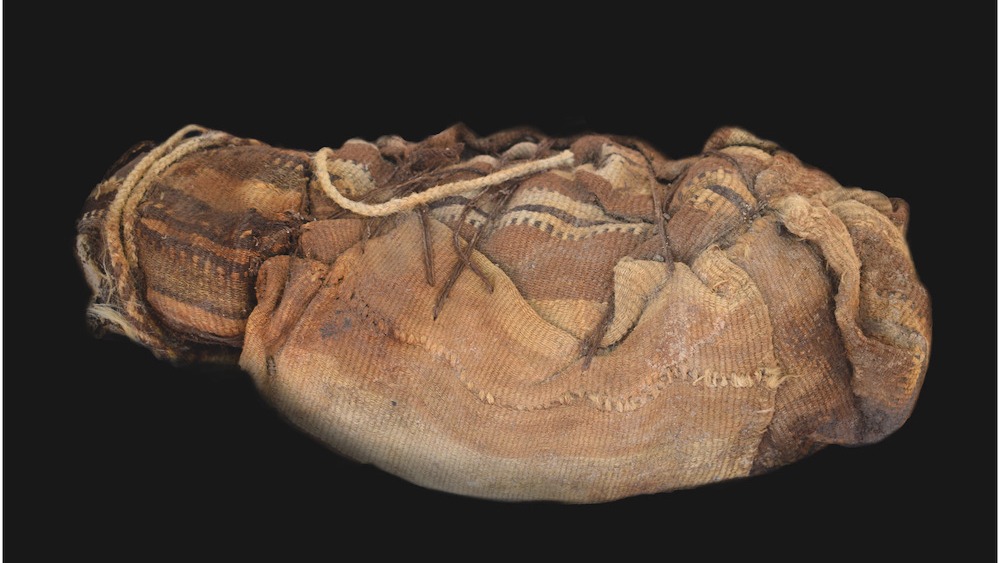
In addition to the human remains, Socha and her team also found a variety of grave goods at the burial sites, including textiles, ceramic pots, weaving tools and a chuspa — a type of bag used for carrying coca leaves.